Heat Pumps
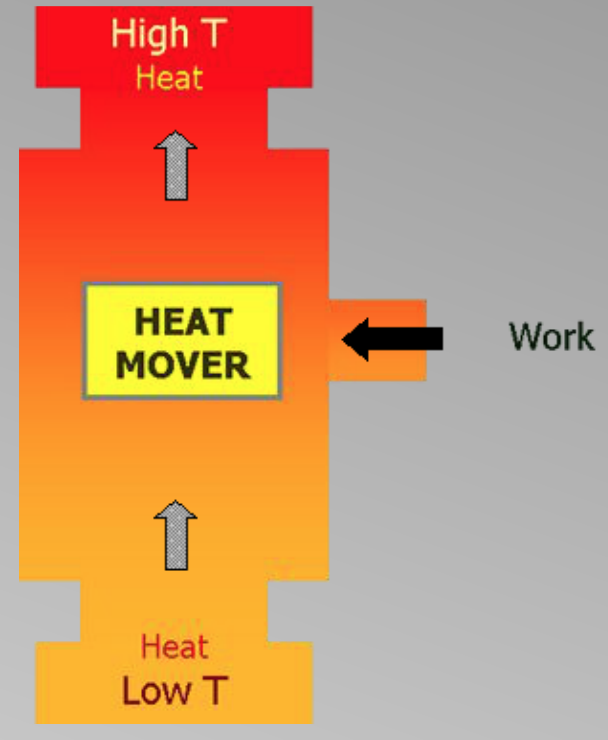
Under natural circumstances, heat only flows from high temperatures to low temperatures. In order to move heat from a low temperature environment to a high temperature environment, work needs to be done (or rather energy needs to be spent).
A device that moves the heat from a low temperature environment to a high temperature environment is called a heat mover.
An example of a heat mover is a heat pump. A heat pump is a heating/cooling system and also a forced-air system. Cooled (and sometimes humidified or electronically cleaned) air is usually delivered through the same ductwork and registers used by heated air.
A heat pump uses air-conditioning principles to extract heat from one place and deliver it to another, and vice versa. In addition to expelling heat from indoors, the system can be reversed to heat the home in the winter. Thus, a heat pump is a device that moves heat from a low-temperature to a high-temperature environment with the help of work that is put in.
Heat pumps are classified based on the low-temperature heat source:
- Air-source heat pump or Air-to-air heat pump. Heat is transferred from the low-temperature air outside to the high-temperature interior.
- Ground-source heat pump or Ground-to-air heat pump. The earth is used as a heat sink in the summer and a heat source in the winter; the pump relies on the relative warmth of the earth for its heating and cooling production.
- Water-source heat pump or Water-to-air heat pump. Heat is transferred from low-temperature water outside (from a pond or a lake) to a high-temperature interior.

An air conditioner is a cooling system and also a forced-air system. It runs on electricity and removes heat from the air with basic refrigeration principles.