Cut Points
Using a crude TBP curve, cut points are defined as the temperatures that represent the limits of a distillate fraction, as illustrated in Figure 4.11. For example, for kerosene, fraction Ta represents the lower cut point, and Tb represents the upper cut point in Figure 4.11.
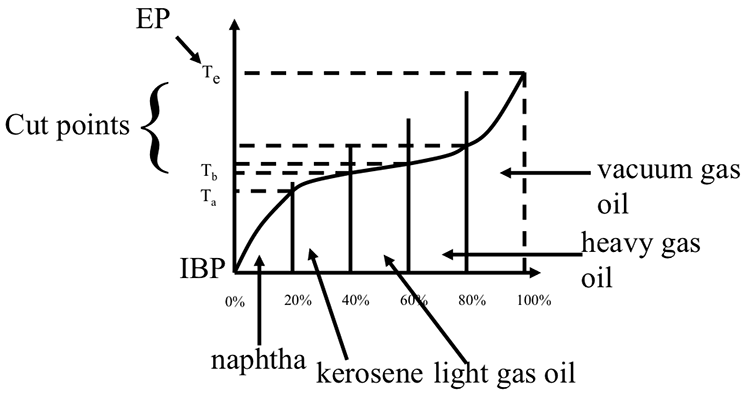
Boiling ranges between the cut points represent distillate products, such as naphtha, kerosene, light gas oil, etc. The difference between the cumulative volume percent at upper and lower cut points is reported as the yield (in volume %) for the particular distillate fraction. For example, for the crude represented in Figure 4.11, the kerosene yield can be calculated as 40%(at Tb) -20% (Ta) = 20% by volume. Table 4.1 shows the TBP cut points for crude oil distillate fractions.
| Distillate Product | Boiling Range |
|---|---|
| Butanes and Lighter | |
| Light SR Naphtha | 90 - 190o F (32-88o C) |
| Heavy Naphtha | 190 - 380o F (88 - 193o C) |
| Kerosene | 380 - 520o F (193 - 271o C) |
| Light Gas Oil | 520 - 610o F (271 - 321o C) |
| Heavy Gas Oil | 610 - 800o F (321 - 425o C) |
| Light Vacuum Gas Oil | 800 - 950o F (425 - 510o C) |
| Heavy Vacuum Gas Oil | 950 - 1050o F (510 - 564o C) |
| Vacuum Residue | > 1050o F (>565o C) |