So much of our discussion about how to address climate change, not only in class this semester but also in general, focuses on the economics of climate change. We talk about how our economic structure created the problem and we talk about the need to create solutions that don't just do the right thing because it's the right thing, but also because it creates economic value. Let's imagine for a minute (well, how about for some of this week, anyway), that what we really need is to re-envision what a healthy economy looks like.
I was first introduced to this concept of doughnut hole economics a few years ago. (You had me at doughnuts, right?) This is a 15 minute TED Talk - required viewing - because Kate Raworth tells this story far better in person than any piece of writing could do.
KATE RAWORTH: Have you ever watched a baby learning to crawl? Because any parent knows, it's gripping. First, they wriggle about on the floor, usually backwards. But then, they drag themselves forwards. And then, they pull themselves up to stand. And we all clap.
And that simple motion of forwards and upwards, it's the most basic direction of progress we humans recognize. We tell it in our story of evolution as well. From our lolloping ancestors, to Homo Erectus, finally upright, to Homo Sapiens, depicted always a man, always mid stride.
[LAUGHTER]
So no wonder we so readily believe that economic progress will take this very same shape, this ever rising line of growth. It's time to think again, to re-imagine the shape of progress.
Because today, we have economies that need to grow, whether or not they make us thrive. And what we need, especially in the richest countries, are economies that make us thrive whether or not they grow.
Yes, it's a little flip in words hiding a profound shift in mindset. But I believe this is the shift we need to make if we, humanity, are going to thrive here together this century.
So where did this obsession with growth come from? Well, GDP, gross domestic product, it's just the total cost of goods and services sold in an economy in a year.
It was invented in the 1930s, but it very soon became the overriding goal of policy making. So much so that even today, in the richest of countries, governments think that the solution to their economic problems lies in more growth.
Just how that happened is best told through the 1960 classic by W.W. Rostow. I love it so much, I have a first-edition copy. The Stages of Economic Growth: A Non-Communist Manifesto.
[LAUGHTER]
[SNIFFING]
You can just smell the politics, huh?
[LAUGHTER]
And Rostow tells us that all economies need to pass through five stages of growth. First, traditional society, where a nation's output is limited by its technology, its institutions, and mindset.
But then the preconditions for takeoff, where we get the beginnings of a banking industry, the mechanization of work, and the belief that growth is necessary for something beyond itself, like national dignity or a better life for the children.
Then takeoff, where compound interest is built into the economy's institutions and growth becomes the normal condition. Fourth is the drive to maturity, where you can have any industry you want, no matter your natural resource base.
And the fifth and final stage, the age of high mass consumption, where people can buy all the consumer goods they want, like bicycles and sewing machines. This was 1960, remember.
[LAUGHTER]
Well, you can hear the implicit airplane metaphor in this story. But this plane is like no other because it can never be allowed to land. Rostow left us flying into the sunset of mass consumerism.
And he knew it, as he wrote, "And then the question beyond, where history offers us only fragments. What to do when the increase in real income itself loses its charm?"
He asked that question, but he never answered it. And here's why. The year was 1960, he was an advisor to the presidential candidate John F. Kennedy who was running for election on the promise of 5% growth.
So Rostow's job was to keep that plane flying, not to ask if, how, or when it could ever be allowed to land. So here we are, flying into the sunset of mass consumerism, over half a century on with economies that have come to expect, demand, and depend upon unending growth. Because we are financially, politically, and socially addicted to it.
We're financially addicted to growth because today's financial system is designed to pursue the highest rate of monetary return. Putting publicly-traded companies under constant pressure to deliver growing sales, growing market share, and growing profits.
And because banks create money as debt, bearing interest, which must be repaid with more. We're politically addicted to growth because politicians want to raise tax revenue without raising taxes. And a growing GDP seems a sure way to do that. And no politician wants to lose their place in the G20 family photo.
[LAUGHTER]
But if their economy stops growing while the rest keep going, well, they'll be booted out by the next emerging powerhouse.
And we are socially addicted to growth because thanks to a century of consumer propaganda, which, fascinatingly, was created by Edward Bernays, the nephew of Sigmund Freud, who realized that his uncle's psychotherapy could be turned into very lucrative retail therapy if we could be convinced to believe that we transform ourselves every time we buy something more.
None of these addictions are insurmountable. But they all deserve far more attention than they currently get. Because, look where this journey has been taking us.
Global GDP is 10 times bigger than it was in 1950. And that increase has brought prosperity to billions of people. But the global economy has also become incredibly divisive, with the vast share of returns to wealth now accruing to a fraction of the global 1%.
And the economy has become incredibly degenerative, rapidly destabilizing this delicately balanced planet on which all of our lives depend. Politicians know it, and so they offer new destinations for growth.
You can have green growth, inclusive growth, smart, resilient, balanced growth. Choose any future you want, so long as you choose growth.
I think it's time to choose a higher ambition, a far bigger one. Because humanity's 21st century challenge is clear. To meet the needs of all people within the means of this extraordinary, unique, living planet so that we and the rest of nature can thrive.
Progress on this goal isn't going to be measured with a metric of money. We need a dashboard of indicators. And when I sat down to try and draw a picture of what that might look like, strange though this is going to sound, it came out looking like a doughnut. I know. I'm sorry.
But let me introduce you to the one doughnut that might actually turn out to be good for us. So imagine humanity's resource use radiating out from the middle. That hole in the middle is a place where people are falling short on life's essentials.
They don't have the food, healthcare, education, political voice, housing that every person needs for a life of dignity and opportunity. We want to get everybody out of the hole, over the social foundation, and into that green doughnut itself.
But-- and it's a big but-- we cannot let our collective resource use overshoot that outer circle, the ecological ceiling. Because there, we put so much pressure on this extraordinary planet that we begin to kick it out of kilter.
We cause climate breakdown. We acidify the oceans, a hole in the ozone layer. Pushing ourselves beyond the planetary boundaries of the life-supporting systems that have, for the last 11,000 years, made Earth such a benevolent home to humanity.
So this double-sided challenge to meet the needs of all within the means of the planet invites a new shape of progress. No longer this ever-rising line of growth, but a sweet spot for humanity. Thriving in dynamic balance between the foundation and the ceiling.
And I was really struck, once I had drawn this picture, to realize that the symbol of well-being in many ancient cultures reflects this very same sense of dynamic balance. From the Maori Takarangi to the Taoist yin yang, the Buddhist endless knot, the Celtic double spiral.
So can we find this dynamic balance in the 21st century? Well, that's a key question. Because as these red wedges show, right now, we are far from balance, falling short and overshooting at the same time.
Look in that hole. You can see that millions or billions of people worldwide still fall short on their most basic of needs. And yet, we've already overshot at least four of these planetary boundaries, risking irreversible impacts of climate breakdown and ecosystem collapse.
This is the state of humanity and our planetary home. We, the people of the early 21st century, this is our selfie. No economist from last century saw this picture. So why would we imagine that their theories would be up for taking on its challenges?
We need ideas of our own, because we are the first generation to see this and probably the last with a real chance of turning this story around. You see, 20th-century economics assured us that if growth creates inequality, don't try to redistribute. Because more growth will even things up again.
If growth creates pollution, don't try to regulate. Because more growth will clean things up again. Except, it turns out, it doesn't and it won't. We need to create economies that tackle this shortfall and overshoot together by design.
We need economies that are regenerative and distributive by design. You see, we've inherited degenerative industries. We take Earth's materials, make them into stuff we want, use it for a while-- often only once-- and then throw it away. And that is pushing us over planetary boundaries.
So we need to bend those arrows around, create economies that work with and within the cycles of the living world. So that resources are never used up, but are used again and again. Economies that run on sunlight, where waste from one process is food for the next.
And this kind of regenerative design is popping up everywhere. Over 100 cities worldwide, from Quito to Oslo, from Harare to Hobart, already generate more than 70% of their electricity from sun, wind, and waves.
Cities like London, Glasgow, Amsterdam are pioneering circular-city design, finding ways to turn the waste from one urban process into food for the next. And from Tigray, Ethiopia to Queensland, Australia, farmers and foresters are regenerating once barren landscape so that it teams with life again.
But as well as being regenerative by design, our economies must be distributive by design. And we've got unprecedented opportunities for making that happen. Because 20th century centralized technologies, institutions, concentrated wealth, knowledge, and power in few hands.
This century, we can design our technologies and institutions to distribute wealth, knowledge, and empowerment to many. Instead of fossil-fuel energy and large-scale manufacturing, we've got renewable energy networks, digital platforms, and 3D printing.
200 years of corporate control of intellectual property is being upended, by the bottom up, open-source, peer to peer, knowledge commons.
And corporations that still pursue maximum rate of return for their shareholders, well, they suddenly look rather out of date next to social enterprises that are designed to generate multiple forms of value and share it with those throughout their networks.
If we can harness today's technologies, from AI, to blockchain, to the internet of things, to material science, if we can harness these in service of distributive design, we can ensure that healthcare, education, finance, energy, political voice reaches and empowers those people who need it most. You see, regenerative and distributive design create extraordinary opportunities for the 21st-century economy.
So where does this leave Rostow's airplane ride? Well, for some, it still carries the hope of endless green growth. The idea that thanks to de-materialization, exponential GDP growth can go on forever while resource use keeps falling.
But look at the data. This is a flight of fancy. Yes, we need to de-materialize our economies. But this dependency on unending growth cannot be decoupled from resource use on anything like the scale required to bring us safely back within planetary boundaries.
I know this way of thinking about growth is unfamiliar because growth is good, no? We want our children to grow, our gardens to grow. Yes. Look to nature and growth as a wonderful, healthy source of life. It's a phase. But many economies, like Ethiopia and Nepal today, may be in that phase. Their economies are growing at 7% a year.
But look again to nature. Because from your children's feet to the Amazon forest, nothing in nature grows forever. Things grow, and they grow up, and they mature. And it is only by doing so that they can thrive for a very long time.
We already know this. If I told you my friend went to the doctor who told her she had a growth, well, that feels very different. Because we intuitively understand that when something tries to grow forever within a healthy, living, thriving system, it is a threat to the health of the whole.
So why would we imagine that our economies would be the one system that could buck this trend and succeed by growing forever? We urgently need financial, political, and social innovations that enable us to overcome this structural dependency on growth so that we can instead focus on thriving in balance within the social and the ecological boundaries of the doughnut.
And if the mere idea of boundaries makes you feel, well, bounded, think again. Because the world's most ingenious people turn boundaries into the source of their creativity, from Mozart on his five-octave piano, Jimi Hendrix on his six-string guitar, Serena Williams on a tennis court.
It's boundaries that unleash our potential. And the doughnut's boundaries unleash the potential for humanity to thrive, with boundless creativity, participation, belonging, and meaning. It's going to take all the ingenuity that we have got to get there. So bring it on. Thank you
Ms. Raworth does a far better job in her TED Talk of describing this concept, but allow me to summarize. The green doughnut you see represents a good life. We're living under our ecological ceiling (so not overexploiting our natural resources) and we're living on a strong social foundation which ensures quality life for all. But this concept isn't playing out in reality, and the words described in the outermost layer of the diagram represent what happens when we overshoot those ecological limits - climate change, ocean acidification, loss of biodiversity - big, complex environmental problems we're facing right now. The concepts described at the core of the diagram suffer when we fail to secure our social foundation - health, education, equality. As you might imagine, we're overshooting the ecological ceiling and we don't have the greatest social foundations, so our doughnut is crumbling from both sides. Ms. Raworth argues (rather effectively) that this mismatch between what we need for balance in our natural world and what we see playing out in society is due largely to our economic structure. And this makes sense if you think about it - if we've predicated 'success' on the idea of growth, where does that end?
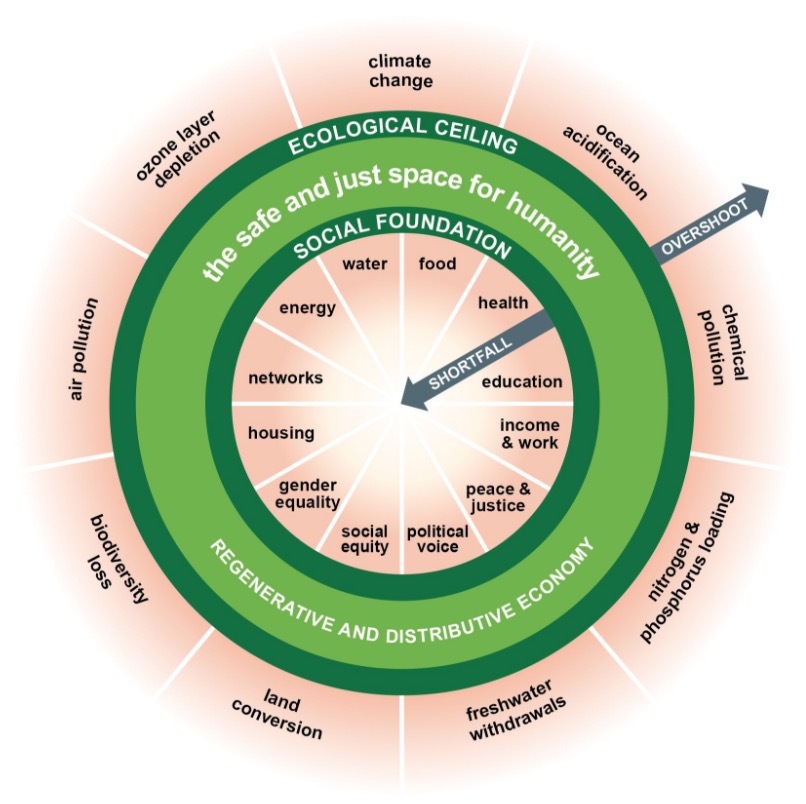
The center of the image is a ring shape labeled "the safe and just space for humanity" and "regenerative and distributive economy.
The inside edge of the ring is labeled "social foundation" and inside the center of the ring is; water, food, health, education, income & work, peace & justice, political voice, social equity, gender equality, housing, networks, and energy. An arrow pointing toward the center of the ring is labeled "shortfall".
The outer edge of the ring is labeled "ecological ceiling". Outside the ring, there are sections labeled; air pollution, ozone layer depletion, climate change, ocean acidification, chemical pollution, nitrogen & phosphorous loading, freshwater withdrawals, land conversion, and biodiversity loss. An arrow pointing away from the ring is labeled "overshoot".
