Modeling Earth
From a young age, we are generally taught that Earth is a sphere. Images such as those taken from space (e.g., Figure 5.1.1) serve to reinforce this idea. Yet, this is an oversimplification—Earth's actual shape is more complicated than the spherical shape it appears to be.
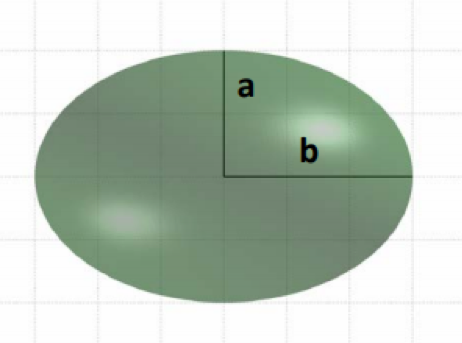
Due to the centrifugal force created by Earth’s rotation, Earth bulges slightly at the center—it is wider around the equator than from pole to pole. Because of this, a better way to describe Earth’s shape is as an ellipsoid. Ellipsoids which closely resemble spheres are often called spheroids—and as Earth is wider in the East-West direction, the most precise word to describe the approximation of Earth's shape is oblate spheroid (or oblate ellipsoid). In literature about this topic, the terms spheroid and ellipsoid are often used interchangeably. The term you use is less important than your understanding of the general concepts involved.
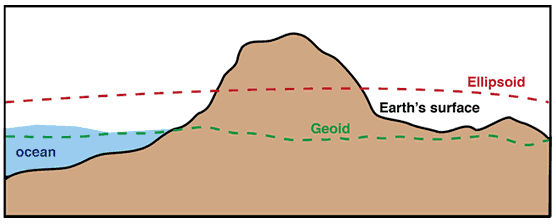
Though the terms ellipsoid or oblate spheroid better describe Earth’s surface than the term sphere, this is still an over-simplification. Due to gravitational forces and natural landforms, the Earth is not perfectly smooth. A very complex mathematical model has been developed to precisely model Earth's surface, but this is of little practical use in cartography so we will not discuss that model here. The most precise model of the Earth which is of practical use to cartographers is the one called the geoid.
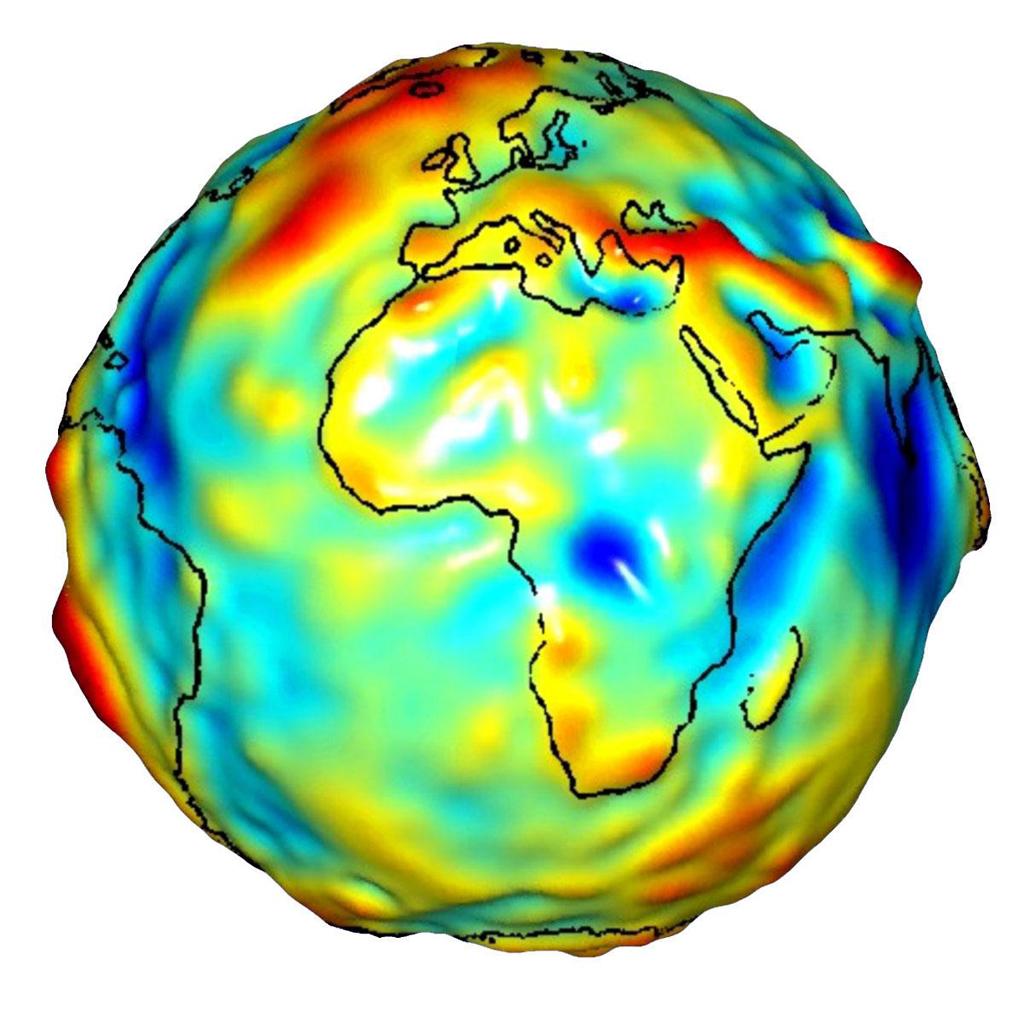
The geoid is defined as “a smooth, undulating surface the Earth would take on if the oceans were allowed to flow freely over the continents—without currents, tides, waves, and so on—which would create a single undisturbed water body” (Slocum et al. 2009, pg. 125). It is an uneven surface which approximates mean sea level across the Earth’s surface by taking gravitational forces into account.
The geoid is constantly changing—due both the ever-changing nature of Earth’s surface (e.g., from continental shifts), and because technological advancements have allowed for more and more precise calculations over the years. The dynamics of Earth and the imprecision of measurement techniques mean that any model of the geoid is only an approximation—and mean sea level itself remains an approximation for Earth’s surface in reality.
Recommended Reading
- Chapter 8: The Earth and Its Coordinate System. Slocum, Terry A., Robert B. McMaster, Fritz C. Kessler, and Hugh H. Howard. 2009. Thematic Cartography and Geovisualization. Edited by Keith C. Clarke. 3rd ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.