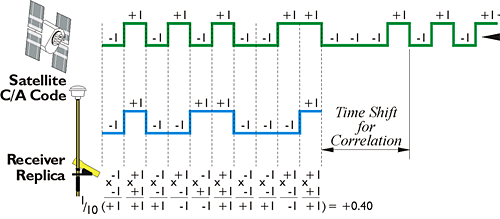
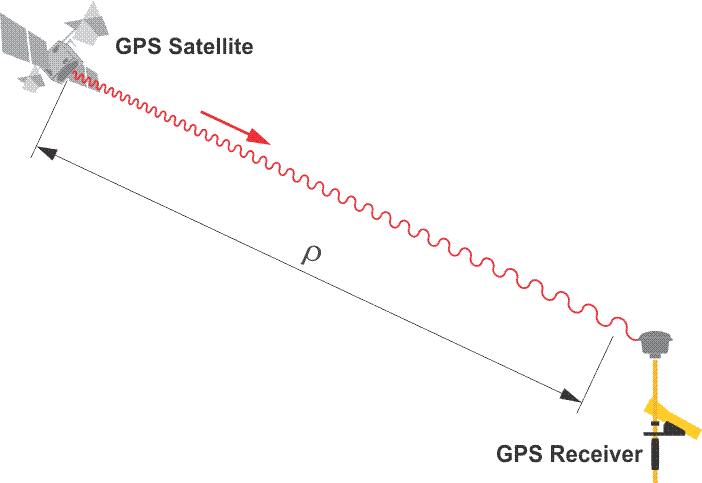
The word observable is used throughout GPS literature to indicate the signals whose measurement yields the range or distance between the satellite and the receiver. The word is used to draw a distinction between the thing being measured, "the observable" and the measurement, "the observation." In GPS, there are two types of observables. The codes are one type of observable. We've talked about how that is modulated onto the carrier. There's another type of observable. That's the carrier itself without the codes. The carrier is the basis of the techniques used for high-precision GPS surveys. In the upper image, you see the pseudorange code observable illustrated as square waves of code states, and in the lower image, you see the carrier wave observable, which is just a constant sine wave, not modulated. The code solution provides a pseudorange. The pseudorange can serve applications when virtually instantaneous point positions are required or relatively low accuracy will suffice. These basic observables can also be combined in various ways to generate additional measurements that have certain advantages. It is in this latter context that pseudoranges are used in many GPS receivers as a preliminary step toward the final determination of position by a carrier phase measurement. Many GPS receivers use the pseudorange code observable as sort of the front door, a way to begin the determination of a position, and then, frequently, they switch to the carrier to refine that position. The foundation of pseudoranges is the correlation of code carried on a modulated carrier wave received from a GPS satellite with a replica of that same code generated in the receiver. Most of the GPS receivers used for surveying applications are capable of code correlation. That is, they can determine pseudoranges. These same receivers are usually capable of determining ranges using the unmodulated carrier, as well. However, first let us concentrate on the pseudorange.