What is Causing Global Warming?
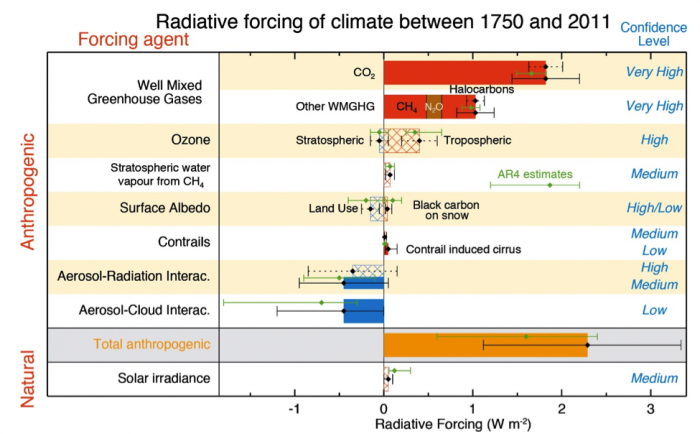
While it is not our intent in this module to explore this question in detail, it is worth pointing out that many human activities clearly affect the climate system. Most notably, emissions of greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide and methane, are causing more heat to be trapped within Earth’s atmosphere. This effect, called the greenhouse effect, has been well understood since it was discovered by Svante Arrhenius in 1896. Figure 1 below, taken from the 2014 IPCC Working Group 1 Technical Summary shows the relative amount of heating or cooling of the climate system that can be attributed to the various factors that have changed between 1750 and 2011. Solar irradiance (bottom) is the one natural factor that has changed measurably (if only slightly), contributing a small amount to warming. The anthropogenic modifications to the climate system, enumerated in the top 7 rows of the figure, and summed in the either (gold) bar of the figure, greatly outweigh the changes due to natural changes in solar irradiance. The IPCC is quite careful to note the level of confidence associated with any given piece of knowledge (see confidence levels indicated on the right side of figure 1). They are also transparent and are quick to point out when new understanding has significantly changed estimates or predictions, as has happened with our understanding of stratospheric water vapor, which was thought to be a significant contributor to warming in the Fourth IPCC Assessment Report (AR4, released in 2007), but has recently been found to be less significant.
Learning Checkpoint
According to Figure 1 above, total warming (i.e., positive radiative forcing) caused by human activities between 1750 and 2011 is equivalent to about:
(a) 0 W/m2
(b) 1 W/m2
(c) 2 W/m2
(d) 3 W/m2
(e)This cannot be determined from the graph.
ANSWER: (c) 2 W/m2
According to Figure 1, total warming (i.e., positive radiative forcing) caused by natural processes between 1750 and 2011 is equivalent to about:
(a) 0 W/m2
(b) 1 W/m2
(c) 2 W/m2
((d) 3 W/m2
(e)This cannot be determined from the graph.
ANSWER: (a) 0 W/m2
According to Figure 1, total warming (i.e., positive radiative forcing) caused by natural processes between 1750 and 2011 is equivalent to about:
According to Figure 1, the single biggest anthropogenic contributor to global warming is:
(a) Greenhouse gas emissions
(b) Changes in surface albedo
(c) Aerosol emissions
(d) Tropospheric ozone emissions
ANSWER: (a) Greenhouse gas emissions
According to Figure 1, the biggest anthropogenic contributor to global cooling is:
(a) Greenhouse gas emissions
(b) Changes in surface albedo
(c) Aerosol emissions
(d) Tropospheric ozone emissions
ANSWER: (c) Aerosol emissions
