Look at the table below to learn about six types of insulation.
| Insulation | What is it made of? | What does it look like? | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|
Fiberglass
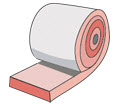 |
Molten glass spun into microfibers | Pink or yellow in the form of batts or rolled blankets. | |
Rock Wool
 |
Rock | Gray or brown fibers in batts or blankets or as shredded loose-fill. | Manufactured in a similar way as fiberglass, but with molten rock instead of glass. |
Cellulose
 |
Recycled paper – newsprint or cardboard shredded into small bits of fiber. | Blown in as loose fill. | It is treated with fire- and insect-resistant chemicals. |
Rigid Foam
 |
Different types, but some made from post-consumer recycled content from fast food containers and cups. | Rigid sheets that are applied directly to framing. | Best where space is limited, but a high R-value is needed. Can be installed on the interior of a wall, but if installed inside, must be covered by a fire resistant material like wallboard. One drawback to foam is it deteriorates unless it is protected from prolonged exposure to sunlight and water. It is also more expensive than other insulation. |
Synthetic Insulation
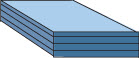 |
Usually polystyrene or polyurethane foam. | Polystyrene comes as rigid boards, and Polyurethane comes as rigid boards or sprayed in place systems. | Polystyrene is used for insulating basements, cathedral ceilings, or sidewalls. Polyurethane foams are high performance insulating materials. |