Fossil fuels are hydrocarbons comprised primarily of the following elements: carbon and hydrogen and some sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen, and mineral matter. Mineral matter turns into ash when burnt.
The composition and the amounts of these elements change for different fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, and natural gas), but the elements are the same. For example, there is more hydrogen in liquid fuels than in coal per unit mass.
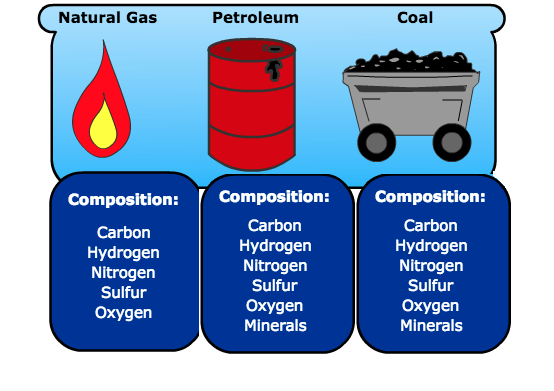
Natural gas is composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen.
Petroleum is composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and minerals.
Coal is composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and minerals.
Combustion is rapid oxidation of the fossil fuel’s elements resulting in the generation of heat. When these elements oxidize (or combine with oxygen), products of combustion are formed.
Instructions: Click on the purple hot spot shown above the piece of coal below to determine what products are formed from each during combustion.