Deregulation or restructuring?
The terms “deregulation” and “restructuring” are sometimes used interchangeably to describe the changes in the electric power industry starting in the 1990s. While the terms are not interchangeable, both in fact are correct. The generation segment of the electricity supply chain has been progressively deregulated, with power plants competing with one another in many areas of the world to provide service to a regional grid operator. Electric transmission has largely been restructured, not deregulated, with transmission regulation shifting from a local to a regional scale. In the U.S., this has meant that the regulation of electric transmission has shifted from state to federal authorities. Electric distribution has, with few exceptions, retained the same regulated structure that it has always had. This “last mile” of wires service is provided by a public utility that is granted a local monopoly in exchange for rate of return regulation by the state. In states that have undertaken deregulation and/or restructuring, the “electric utility” is in many cases just a distribution company.
Please read the first two sections from Blumsack, Measuring the Benefits and Costs of Regional Electric Grid Integration, which describes in more detail the process of deregulation/restructuring and some of the important U.S. federal policy initiatives that have pushed the industry towards its new state. It is important to realize that some aspects of restructuring have essentially arisen from federal initiatives and some from state initiatives. The most important aspects of electricity restructuring are:
- The vertical disintegration of the electric utility into separate generation, transmission and distribution companies. In some jurisdictions, this has been accompanied by the divestiture of generation plants by the former utility company.
- The establishment of “open-access” transmission regulations at the federal level, requiring all transmission-owning companies to offer non-discriminatory access to their transmission grids. This measure is aimed at promoting regional competition between generators.
- The creation of competitive wholesale markets for electric energy through the creation of “Regional Transmission Organizations.” These entities will be discussed further later in this lesson.
- Some states have opened up retail generation service to competitive forces. In these states, consumers purchase transmission and distribution service from the utility but have the option to purchase generation service from a company other than the utility. If this model sounds confusing, it is actually very similar to how telecommunications was deregulated in the 1980s, where you got to choose your long-distance phone company, but local calls were handled by your telephone utility.
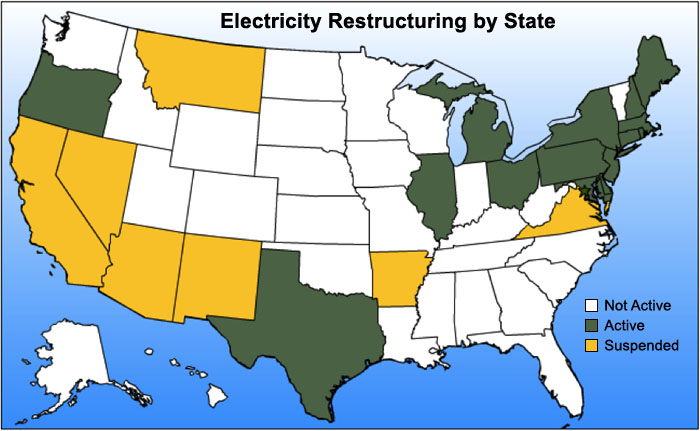
Not all areas of the U.S. have adopted deregulation or restructuring. Figures 11.3 and 11.4 show the areas of the U.S. that have adopted competitive wholesale markets for electric energy generation and those individual states that have taken on power-sector reforms at the retail level.
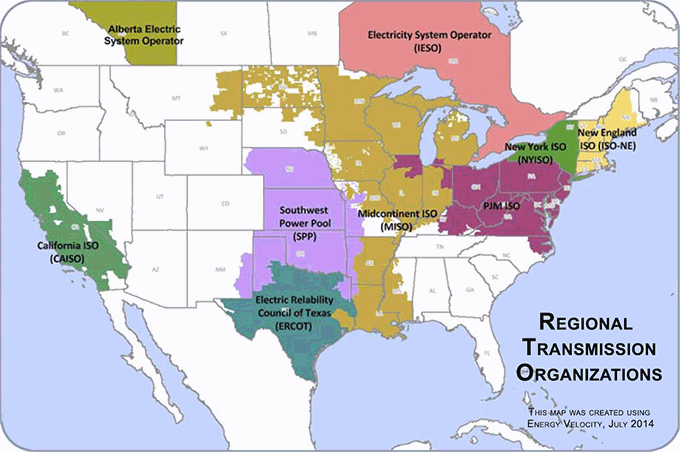
- California ISO, which includes CA and part of SW Nevada.
- Electric Relability Council of Texas (ERCOT), which includes most of TX.
- Southwest Power Pool (SPP), which includes a portion of N. TX, all of OK, KS, most of Nebraska, and western pieces of MO, AK, and the NW tip of LA.
- Midcontinent ISO (MISO), which contains portions of the following states: LA, AK, MS, MO, IL, IN, IA, MI, WI, MN, ND, SD, MT.
- PJM ISO, which includes portions of KY, VA, WV, WI, IL, IN, MI, and all of OH, PA, NJ, MD, and DE.
- New York ISO (NYISO), which includes all of NY.
- New England ISO (SO-NE), which contains all of CT, MA, RI, NH, VT, and most of ME.
- Electricity System Operator (IESO), which contains portions or all of Ontario, Canada.
- Alberta Electric System Operator, which contains portions or all of Alberta, Canada.