Acid Gas Removal
Sour gas separated in the Gas Processing unit is sent to the Amine Unit for acid gas removal using chemical solvents such as monoethanolamine (MEA), or diethanolamine (DEA), as shown in Figure 10.2.
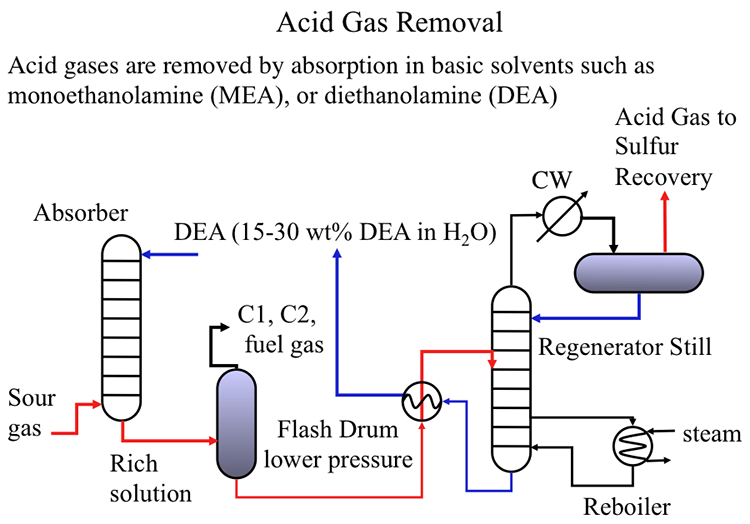
As shown in Figure 10.2, the sour gas is pumped from the bottom of an absorption column to get in contact with the basic solution (typically 15-30wt% diethanolamine) to capture H2S (and other acidic gases such as CO2) in the solution. The rich solution containing the acid gases is sent to a flash drum to recover the C1 and C2 hydrocarbons from the rich solution to be used as fuel gas in the refinery to generate process heat, or steam in fired furnaces. The rich solvent is then sent to a regenerator still to remove the acid gases that are sent to the sulfur recovery unit. The remaining solvent is cooled in a heat exchanger and recycled to the absorption unit to close the loop [2].
[2] Petroleum Refining, by J. H. Gary, G. E. Handwerk, M. J. Kaiser, 5th Edition, CRC Press NY, 2007, Chapter 13, Supporting Processes, pp. 280-283.