Network analysis can be used to solve many different transportation problems that would be very challenging to solve otherwise. A prerequisite to performing network analysis is that you have a network model. In ESRI’s terms, this is a network dataset. We walked through an exercise to construct a network dataset in the last lesson. Of course, it is not a requirement of network analysis that you construct your own network model. There are a number of commercially available network models you can use instead.
The types of problems which network analysis can be used to solve are quite varied. One common characteristic of the algorithms that power each is that they involve determining the cost of one or more routes through the network. The cost is most commonly based on time or distance, but you can define a cost attribute any way you want. For example, you might score each edge in the network based on its scenic value. You could then create a cost parameter based on the scenic score and use the solver to find the most scenic route.
ESRI provides 6 out-of-the-box network analyses as a part of Network Analyst. ESRI terms these network analyses “solvers.” The solvers are listed below along with a brief description of each:
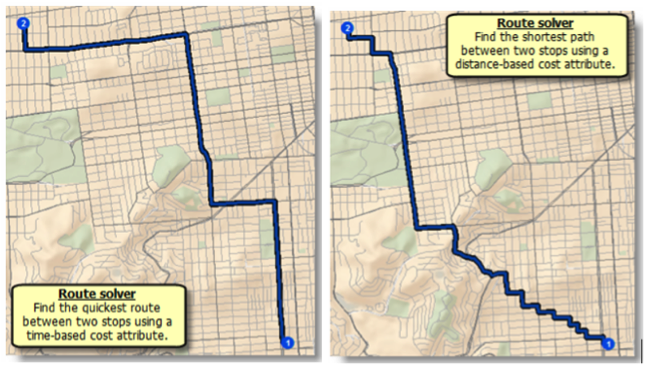
Route Solver
The route solver determines the best route between two or more points. Most of us use this network analysis on a regular basis. Whenever you use Google Maps or a comparable service to get directions from one location to another the service is conducting a network analysis to determine the best, typically fastest, route. This solver can route any number of points according to a specified order (i.e., the traveling salesman problem) or the most efficient order.
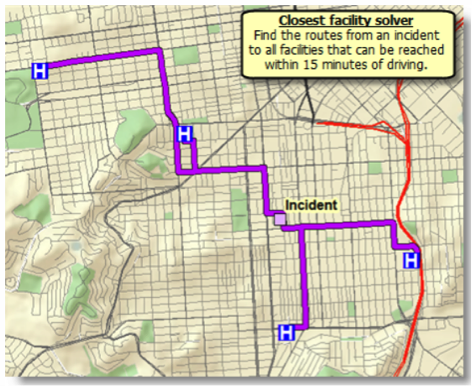
Closest Facility Solver
This solver is used to determine the closest facility to a given location. The term "facility" can be a bit misleading. For example, this solver could be used to determine the closest ambulance to an accident scene. In this case, using ESRI’s terminology, the ambulances would be considered facilities.
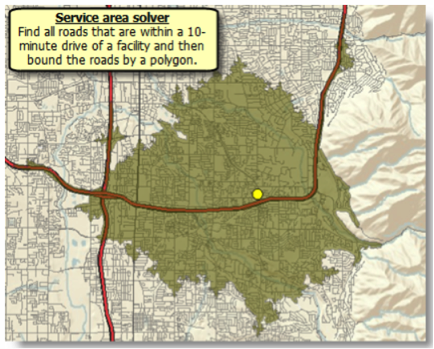
Service Area Solver
The geographic region which can reach a designated facility in a certain period of time (or vice versa) is termed a service area. To determine the bounds of this area, you can use the Service Area Solver.
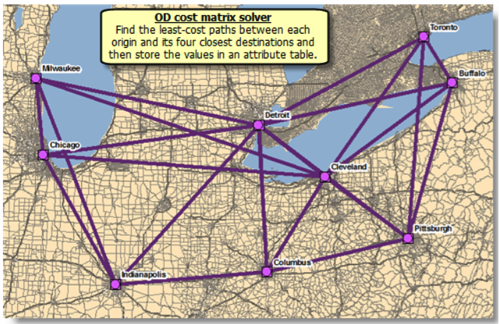
Origin-Destination (OD) Cost Matrix Solver
The OD cost matrix solver is generally used to determine the distances of the fastest routes between a set of origins and a set of destinations. Although the path between each origin and destination is often represented as a straight line, the route which corresponds to the time and distance costs between each pair of locations follows the street network.
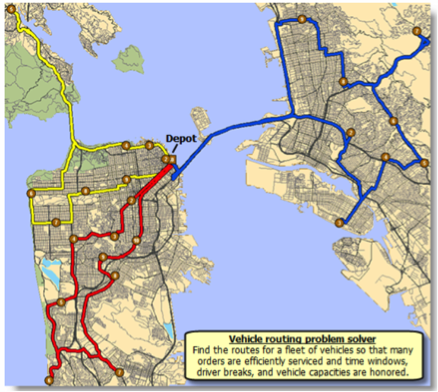
Vehicle Routing Solver
The vehicle routing solver is typically used to determine the most efficient routes for a fleet of vehicles tasked with servicing a series of stops.
Location-Allocation Solver
The location-allocation solver can be used to determine how effectively a facility site is servicing locations which have a need for its services. As such, it can be used to select the best location for a facility from a series of candidate locations.