A Little Light Physics of Energy
When physicists talk about “energy,” they are talking about the “ability or capacity to do work.” Physicists, in a triumph of circular logic, define “work” as a change in energy. To normal people, “work” involves a large range of tasks involving heat or motion – everything from getting out of bed to powering a cruise ship. Virtually every aspect of our daily lives involves “work” and therefore energy in some form. To measure the total amount of work done (and thus the total amount of energy utilized), physicists use the joule (J). In the United States and the United Kingdom, the British thermal unit (Btu) is also commonly used. The Btu is technically defined as the amount of energy required to heat one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. There are approximately one thousand Joules in one Btu. Power is the rate at which work is done and is measured in watts (W) or joules per second.
In the non-physics world, however, energy is a derived demand—that is, people don't really demand energy. Instead, they demand goods and services that require energy to be produced or provided.
In the world of physics, there are several forms of energy including:
- Mechanical energy, which involves motion and changes in speed.
- Chemical energy, which arises from breaking or changing the bonds between molecules which occurs when fossil fuels are burned.
- Thermal energy, which arises from vibrations on an atomic level and which creates heat.
- Electrical energy, which is the movement of charged particles and is associated with batteries and electrical currents.
- Nuclear energy, which holds the nucleus of an atom together.
Energy can, and often does, change from one form into another. For instance, a car battery, which is a form of chemical energy, produces the electrical energy needed to run headlights. Similarly, a diesel locomotive burns diesel fuel to produce the electrical energy needed to drive the engine's wheels.
Complex processes—such as the process of producing electrical energy through the combustion or burning of fossil fuels—typically require several energy transformations or conversions.
In a simple combustion turbine at a power plant, for example, some fuel—such as coal or natural gas—is burned. This breaks the molecular bonds and produces chemical energy. This chemical energy is used to heat water, producing steam or thermal energy (which is why plants that burn fossil fuels are sometimes referred to as “thermal” plants). The steam then turns a generator, producing mechanical energy, which in turn, creates electrical energy. A nuclear power plant works exactly the same way, except the energy to heat water comes from nuclear reactions (fission – the breaking apart of an atom’s nucleus) rather than from combustion of fuel.
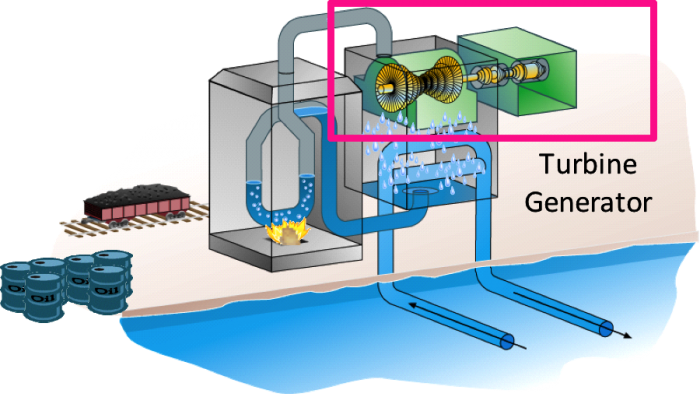
The first law of thermodynamics, also known as conservation of energy, describes these transformations. It states: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only change in form.
But any time an energy conversion occurs, some energy is lost and typically as heat. Think about the heat light bulbs give off or the heat a car engine gives off after being driven. This is the second law of thermodynamics, which says basically that, what you get out of an energy conversion is always less than what you put in.
To return to the power plant, for every unit of fuel that is burned, only about one-third comes out as electric power—which would seem to violate the first law of thermodynamics (the energy content of the input fuel should equal the energy output). So where did the other two-thirds go?
Most of the energy is lost as heat since the steam simply escapes into the atmosphere, which is why large power plants require immense cooling towers. The heat lost out of the cooling tower plus the electricity output of the plant is just about equal to the energy input. Put another way, in terms of capturing thermal energy to turn it into electricity, most of our power plants operate at about 35 percent efficiency.
Newer technologies can reduce the amount of waste heat. Combined-cycle plants capture the exhaust gas and use it to run a second turbine. Combined heat-and-power (CHP) plants use the exhaust gas to heat building spaces or water.
Keep in mind these guiding principles of energy conversion:
- No energy process is completely reversible since some of the energy is lost.
- A machine whose input is mechanical energy can create useful energy (usually electrical energy) with minimal losses. Examples include hydroelectric dams, wind turbines, and alternators.
- A machine whose input is thermal energy can never be 100 percent efficient at creating useful energy. Examples including the burning of fossil fuels, nuclear power plants, and internal combustion engines.