Pipeline Failure Causes
System Type: Gas Distribution
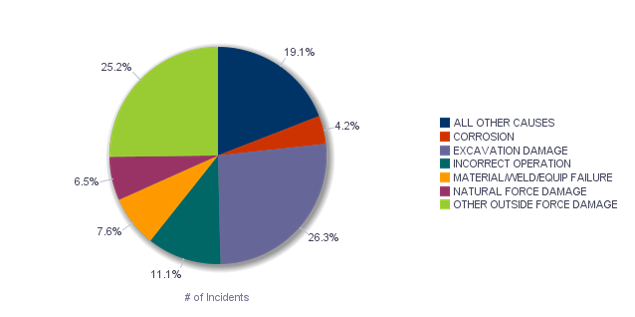
The causes of serious pipeline incidents during gas distribution, broken down by percentage, are 4.2% corrosion, 26.3% excavation damage, 11.1% incorrect operation, 7.6% material/weld/equipment failure, 6.5% natural force damage, 25.2% other outside force damage, and 19.1% all other causes. The pie graph below illustrates this breakdown.
System Type: Gas Transmission
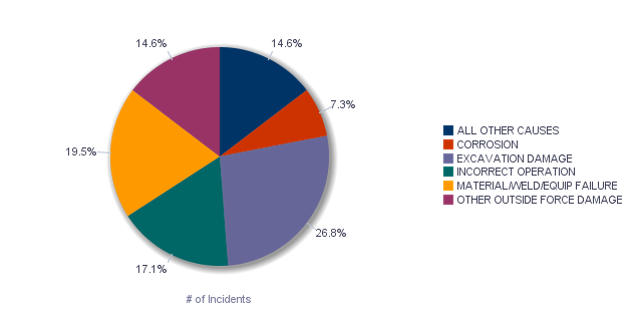
The causes of serious pipeline incidents during gas transmission, broken down by percentage, are 7.3% corrosion, 26.8% excavation damage, 17.1% incorrect operation, 19.5% material/weld/equipment failure, 14.6% other outside force damage, and 14.6% all other causes. The pie graph below illustrates this breakdown.
The U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) are responsible for maintaining industry inspection standards and incident investigation. The leading causes of gas distribution pipelines, primarily in urban and suburban areas, are excavation damage and other outside force damage. These lines are often placed in and around areas that will see construction activity in the future and increase the likelihood of damage from excavation or other outside forces. Transmission lines, on the other hand, are often constructed in rural areas where excavation is less frequent per mile of pipeline, and therefore excavation damage is less likely. The leading causes of incidents in transmission lines are failures due to materials, welds, or equipment.