Asphaltene Yield
Independent variables in the deasphalting process include the solvent used, pressure, temperature, S/R, and contact time. These variables can be controlled to obtain the optimum conditions for the desired separation in deasphalting. One of the important dependent variables in the process is the asphaltene yield. Figure 5.10 shows, in qualitative plots, how asphaltene yield varies as a function of the process parameters.
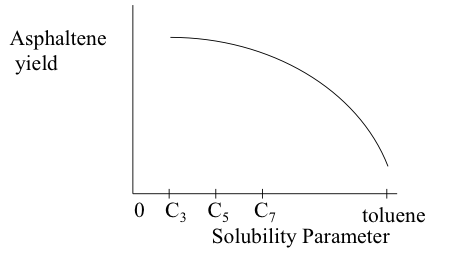
Figure 5.10a. Effect of solubility parameter on asphaltene yield.
Credit: Dr. Semih Eser © Penn State is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
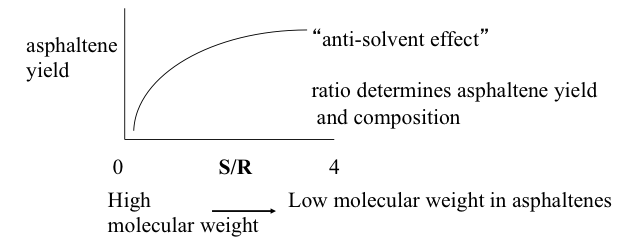
Figure 5.10b. Effect of molecular weight on asphaltene yield.
Credit: Dr. Semih Eser © Penn State is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
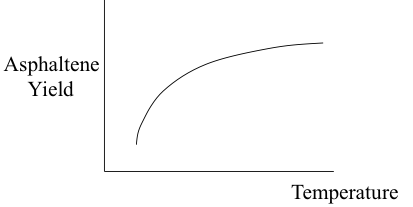
Figure 5.10c. Effect of temperature on asphaltene yield.
Credit: Dr. Semih Eser © Penn State is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
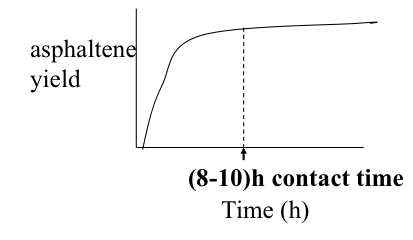
Figure 5.10d. Effect of contact time on asphaltene yield.
Credit: Dr. Semih Eser © Penn State is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0