Batteries are usually installed in groups for PV applications. In this case, the parallel and series connection of batteries is referred to as the Battery Bank. Lead-acid batteries are usually rated at 12 V, 24 V or 48 V. This voltage is determined by the series and parallel interconnection of several batteries. The voltage needs to meet the load or inverter voltage level requirements.
Reflection
How do we determine the battery bank voltage levels for PV applications?
Click on “Click for answer…” to reveal the answer.
ANSWER
12V, 24V, and 48V depending on the PV system size, as will be discussed in Lesson 6.
The series and parallel connection principles are similar to PV modules where we add voltage when connected in series while current is added for parallel connections of batteries. Similar to PV, groups of batteries connected in parallel are called a Battery String. As for the capacity rating of a battery bank, it is similar to the current principle. When connecting batteries in series, the capacity is not added. As for a parallel connection, the capacities add up.
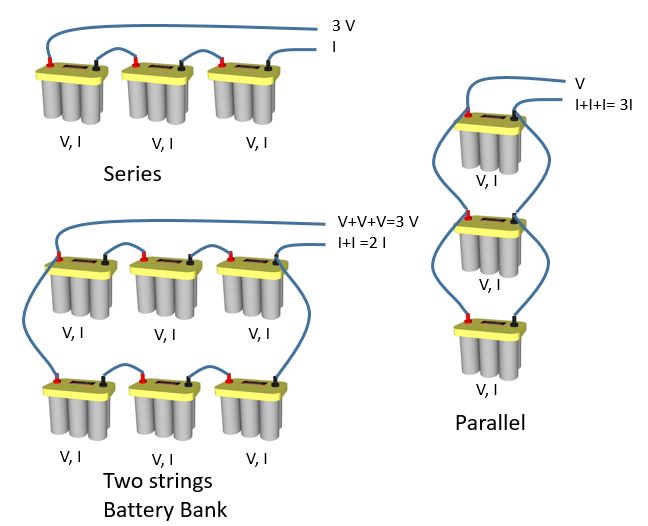
Figure 3.8 illustrates the series and parallel connections of batteries and the corresponding voltage and current. As can be seen, batteries can be connected in series, parallel, or both. In this case, each battery with "V" for voltage and "I" for current is connected either in series or parallel with other similar batteries. The total voltage and current depends on the wiring type. In case of series connection, the total voltage of three batteries will be 3V while the current is similar to the current of a single battery. When three batteries are connected in parallel, the voltage equals the voltage of a single battery, while the total current is the sum of the currents of all batteries for a total of 3I. When two strings of three batteries are connected in parallel, the total voltage will be 3V, while current is summed for the two strings for a total of 2I.
Reflection
What is the total capacity (in Ah) and what is the total energy capacity (in Wh) of the two strings shown in Figure 3.8 if each battery is rated 100Ah?
ANSWER: The total capacity is 200 Ah, while the total energy is 600 wh (assuming each battery is rated at 1 Volt).
It is recommended to have as few battery strings as possible to avoid voltage differences that may create power loss. In larger PV installations where more battery banks are required, it is recommended to connect more batteries in series rather than parallel strings. An example of a mobile bus that is converted to a solar stand-alone system with batteries is shown in Figure 3.9.

Note:
For selection criteria of batteries, please refer to Required Reading Chapter 6, Photovoltaic Systems by James P. Dunlop (text)
Design considerations
When designing a battery bank for a specific location, a good design will ensure that the battery bank is perfectly:
- sized so the energy capacity matches the load requirements.
- sized for maximum and minimum voltage requirements for the desired application.
- ventilated to meet temperature requirements.
- maintained to maximize the utilization of batteries.