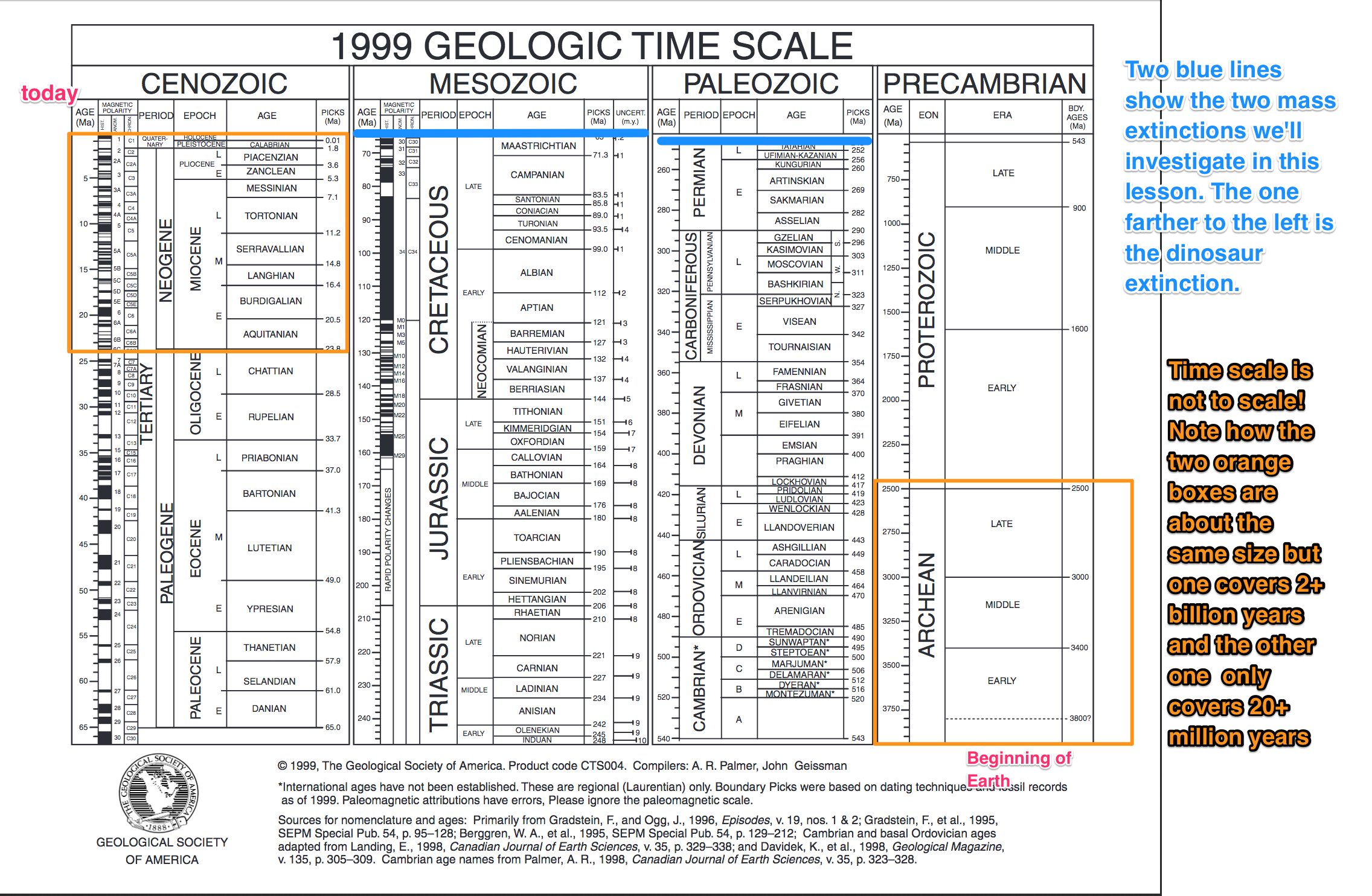
How is geologic time divided?
Geologic mapping involves a certain amount of detective work. Layers of rock preserve a record of the planet's past climate and its biological population. Early versions of the geologic timescale were mostly based on index fossils—these are fossils commonly found in a particular sequence of rock around the world. Finding a certain index fossil meant being able to correlate that rock with other rocks containing that same fossil in other places on Earth. Divisions of time were generally assigned based on the disappearance of index fossils or on changes in rock type at certain points in geologic history. Relative ages of rocks around the world have been cataloged for over a hundred years. However, it has only been since the advent of radiometric dating and paleomagnetic measurements that we have also been able to assign numerical ages to the different divisions.
Here are two versions of the geologic timescale (both are in PDF format):
We do not have perfect preservation of the entire 4.5 billion year history of the planet. Preservation increases towards the present time, as you would expect. Therefore the geologic timescale contains more detailed divisions the closer we get to the present. The first abundant organisms with shells in the fossil record don't even appear until about 542 million years ago, which is a fifth of the way back from the present time. I annoted the second of the two time scales linked above to show where the two extinction events pertinent to this lesson appear in time, and to give you a warning about how the layout isn't to scale.