Acid rain is measured using a pH scale.
pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration, which is measured as a negative logarithm. In other words, acids produce hydrogen ions and alkalis produce hydroxyl ions, so pH is the power of a solution to yield hydrogen ions [H+].
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14 and indicates how acidic or basic a substance is.
- A pH of 7 is neutral.
- A pH less than 7 is acidic.
- A pH greater than 7 is basic.
The lower a substance's pH, the more acidic it is. Each whole pH value below 7 (the neutral point) is ten times more acidic than the next higher value.
- For example, a pH of 4 is ten times more acidic than a pH of 5 and 100 times (10 times 10) more acidic than a pH of 6.
The higher a substance’s pH, the more basic or alkaline it is.
- Each whole pH value above 7 is ten times more alkaline (another way to say basic) than the next lower whole value.
- For example, a pH of 10 is ten times more alkaline than a pH of 9.
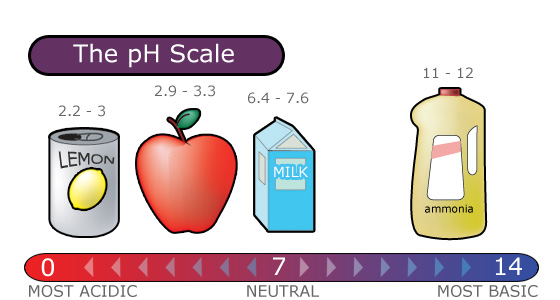
The pH Scale
Credit: Students Diary. "pH & Acid Base| Acid Base Balance." YouTube. February 19, 2022.