For natural gases we are also most interested in the Gas Formation Volume Factor, Bg, and the Gas Viscosity, μg, as these properties strongly influence gas storage (and accumulation) and gas flow. For most reservoir engineering calculations, the gas formation volume factor (and Gas Compressibility, cg, and Gas Density, ρg) can be determined from the Real Gas Law, Equation 3.27:
Where:
- p is the pressure of interest, psi
- V is the volume, ft3
- Z is the oil super-compressibility factor, dimensionless
- R is the gas constant, (psi ft3) / (lb-moles °R)
- T is temperature, °R (°R = °F + 460.67)
Gas Super-Compressibility Factor, Z
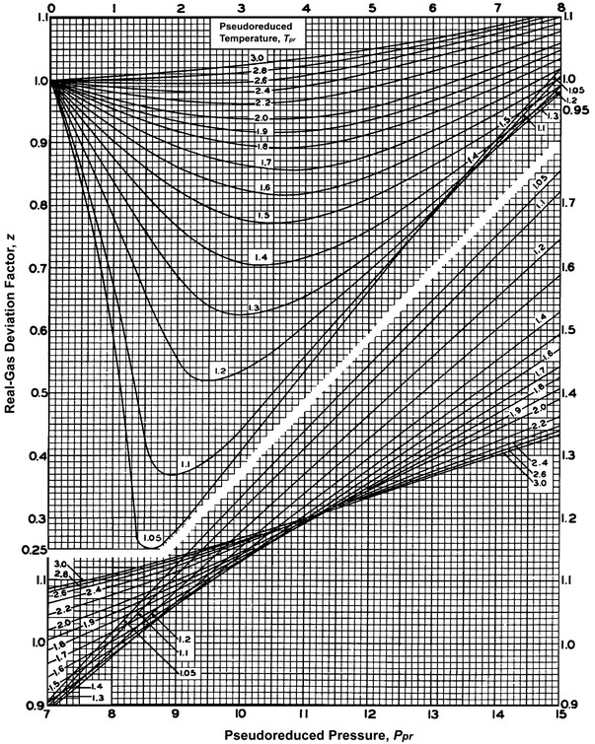
The gas supercompresibility factor, Z (or Z-Factor, or Real Gas Deviation Factor), is a function of pressure and temperature that corrects the Ideal Gas Law for high pressure and high temperature conditions. In the oil and gas industry, the z-factor correlation for hydrocarbon gases that is universally accepted in the Standing-Katz Correlation[12]. This correlation is shown graphically in Figure 3.12.
As illustrated in Figure 3.12 The Standing-Katz Correlation correlates the z-factor to the Pseudo-Reduced Pressure, ppr, and Pseudo-Reduced Temperature, Tpr. The pseudo-reduced properties are defined by:
and
Where:
- p is the pressure of interest, psi
- ppc is the pseudo-critical pressure, psi
- T is temperature of interest, °R
- Tpc is pseudo-critical temperature, °R
All of these properties are called pseudo-properties because the pseudo-critical pressure and pseudo-critical temperature are not the true, measured critical properties, but are calculated properties:
and
with
Where:
- ppc is the pseudo-critical pressure, psi
- Tpc is the pseudo-critical temperature, °R
- ϒg is the gas gravity (MWg/MWair), dimensionless
- MWg is the molecular weight of the gas, lb/lb-mole
- MWair is the molecular weight of air, lb/lb-mole (28.97 lb/lb-mole)
In cases where significant concentrations of inorganic impurities, CO2 and H2S are present, then corrections to Equation 3.61 and Equation 3.61 are required:
and
with
Where:
- ppc corrected is the corrected pseudo-critical pressure, psi
- ppc Eq. 3.61 is the pseudo-critical pressure from Equation 3.61, psi
- Tpc corrected is the corrected pseudo-critical temperature, °R
- Tpc Eq. 3.60 is the corrected pseudo-critical from Equation 3.60, °R
- ϵcorrection is the correction for CO2 and H2S, °R
- yCO2 is the mole fraction of CO2 in the gas phase, fraction
- yH2S is the mole fraction of H2S in the gas phase, fraction
The Standing-Katz[12] correlation has also been mathematically curve fit[13]. The equation for z-factor then becomes:
with
It should be noted that the solution of this equation for the z-factor requires an iteration procedure. This is because the z-factor appears both on the left-hand side of Equation 3.66 and the right-hand side of the equation through the pseudo-reduced density, ρpr. Typically, this is solved with a Newton-Raphson iteration procedure which is beyond the scope of this class. For our purposes, if supercompressibility factors are required, we can simply read the chart to obtain them.
Real Gas Formation Volume Factor, Bg
The Formation Volume Factor, Bg, of a real gas, like its oil phase analog, is used to convert one standard cubic foot, SCF, of gas at reference conditions to its volume at reservoir conditions. For natural gases, in the U.S. domestic oil and gas industry, we use the standard conditions of pSC = 14.7 psi and 60 °F. The gas formation volume factor for a real gas can be calculated directly from the Real Gas Law once we have an estimate of the super-compressibility factor. If we assume one lb-mole of natural gas, then the volume that it would occupy at standard conditions would be (assuming ZSC = 1.0 at standard conditions – a very good assumption):
At reservoir conditions, that same lb-mole would occupy a volume of:
Now, the gas phase formation volume factor we can define as:
There are times when we would like to consider the volume of gas in reservoir barrels, bbl. This is because we have used reservoir barrels as the units for the liquid (oil and water) volumes, and we would like to determine the volume occupied by the gas and liquids combined. We can convert the units of Equation 3.68a by applying the unit conversion constant of 1 bbl = 5.615 ft3:
Where:
- Bg is the gas formation volume factor, ft3/SCF (Equation 3.68a) or bbl/SCF (Equation 3.68b)
- Z is the supercompressibility factor at reservoir conditions, pr and Tr, dimensionless
- Tr is the reservoir temperature, °R
- TSC is the reference (standard) temperature (520 °R in U.S. domestic industry), °R
- pr is the reservoir pressure, psi
- pSC is the reference (standard) pressure (14.7 psi in the U.S. domestic industry), psi
Real Gas Compressibility, cg
The isothermal compressibility of a real gas can also be determined directly from the Real Gas Law. Starting with the definition of isothermal compressibility:
Substituting the Real Gas Law, Equation 3.27, into Equation 3.69:
or
The derivative, , can be calculated by differentiating Equation 3.66 and Equation 3.67 with respect to pressure.
Real Gas Density, ρg
The density of a real gas can also be determined directly from the Real Gas Law. Starting with the Real Gas Law:
Now the number of moles is equal to a mass divided by the molecular weight, n = m / MWg. Substituting into the Real Gas Law:
Now from the definition of gas density and the substitution of the Real Gas Law:
Where:
- ρg is the gas density, lb/ft3
- p is the pressure of interest, psi
- MWg is the molecular weight of the gas, lb/lb-mole
- Z is the supercompressibility factor at reservoir conditions, pr and Tr, dimensionless
- R is the Gas Constant, 10.73 ft3 psi / °R lb-mole
- T is the temperature of interest, °R
Real Gas Specific Gravity, γg
The specific gravity of a real gas can also be determined directly from the Real Gas Law. For gases, the specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the density of the gas to the density of air at standard conditions. Dividing Equation 3.71 written for a gas by Equation 3.71 written for air at standard conditions (Z = 1.0) results in:
Now, the molecular weight of gas is 28.87 lb/lb-mole:
Real Gas Viscosity, μg.
The viscosity of natural gases can be determined by the correlation of Lee, Gonzalez, and Eakin[14]:
with
Where:
- μg is the gas viscosity, cp
- K, X, and Y are correlation coefficients
- ρg is the gas density at the pressure and temperature of interest, gm/cc
- MWg is the molecular weight of the gas, lb/lb-mole
- T is the temperature of interest, °R
[12] Standing, M.B. and Katz, D.L.: "Density of Natural Gases," Trans., AIME (1942) 146, 140-49.
[13] Dranchuk, P.M. and Abou-Kassem, J.H.: "Calculations of z-Factors for Natural Gases Using Equations of State," J. Cdn. Pet. Tech. (July-Sept. 1975) 34-36.
[14] Lee, A.L., Gonzalez, M.H., and Eakin, B.E.: "The Viscosity of Natural Gases," JPT (Aug. 1966) 997-1000; Trans., AIME (1966) 234.