Using the roads raster layer for distance analysis
Distance analysis using a roads raster layer is straightforward. The values in the layer are regarded as 'weights' indicating how much more expensive it is to traverse that cell than if the cell were unweighted. Thus, with the roads layer you just created, traveling on major roads incurs no penalty, traveling on local roads is twice as expensive (takes twice as long), and traveling off-road is very slow indeed (100 times slower). These are not accurately determined weights, but serve to demonstrate the potential of these methods.
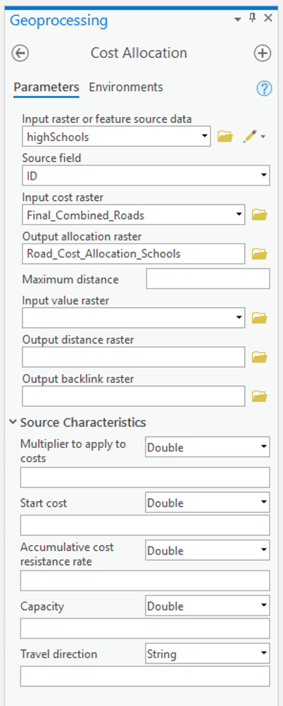
Select the Spatial Analyst Tools - Distance - Cost Allocation tool (Figure 7.10).
Here you are performing another distance analysis, but this time weighted by the roads raster layer you just created. Again, request an Allocation output from the analysis. (You might also be interested to request the Output distance raster to look at the distances that accumulate for each cell.)
Deliverable
Perform the cost-weighted distance analysis for high schools using the roads raster layer. Examine the resulting allocation layer. How does it differ from the straight-line distance allocation result? Do the roads account for all the inconsistencies between the straight-line distance allocation and the actual school districts? Respond to these questions in your Project 7 write-up. Make sure to include the resulting map to support your explanation.